In this article, our AI experts draw on analytics and insights from leading industry reports, including Bank of America, MIT, BCG, the World Economic Forum, and others. We examine current market dynamics and share our perspective on what these trends mean for AI development outsourcing decisions.
- 54% of investors believe AI-related assets are in a bubble, with major providers circulating funds between the same players.
- Despite $30–40 billion in enterprise GenAI investment, 95% of organizations report zero return on investment.
- Most AI adoption failures come down to people, processes, and ways of working—not budget or technology.
- AI-related privacy and security incidents jumped 56.4% in a single year, making data governance a critical risk factor.
- Vendor-led AI projects succeed twice as often as internal builds, making partner selection one of the most consequential decisions in any AI strategy.
- Tightening regulation—including the EU AI Act and DORA—is already affecting tens of thousands of organizations globally.
The "AI bubble" concerns and vendor ecosystem stability
Companies are incorporating AI into their operations at an unprecedented pace. At the same time, growing concerns about a potential "AI bubble" are creating real risks for vendor stability and long-term partnerships.
Three key factors support the bubble argument: unprecedented investment volumes, market concentration, and rapidly rising stock prices among AI companies.
The investment structure among major AI providers raises additional concerns. As NBC News reported in fall 2025, capital flows have created interdependent loops. NVIDIA invests in OpenAI, which purchases cloud computing from Oracle, which buys chips from NVIDIA, holds stakes in CoreWeave, which provides AI infrastructure back to OpenAI.
These deals between OpenAI, NVIDIA, Oracle, AMD, CoreWeave, Intel, and even the US government form a closed investment economy. Funds constantly circulate between the same players. At first glance, everyone wins: OpenAI gets computing resources; NVIDIA gets guaranteed chip sales, and others get capital gains. However, investment bankers and analysts are raising concerns. Many of these deals fuel valuations through mutual obligations rather than creating genuine added value.
Vendor selection and dependency risks
The AI vendor landscape is fragmented and rapidly evolving. Companies must evaluate which providers offer stability and long-term support. The collapse of Builder.ai, once valued at $1.3 billion, highlighted the risks of vendor lock-in and loss of control over source code and data.
Vendor lock-in poses a strategic risk when organizations become so dependent on a single provider that switching is technically, financially, or legally prohibitive.
Operational implementation risks and roadblocks
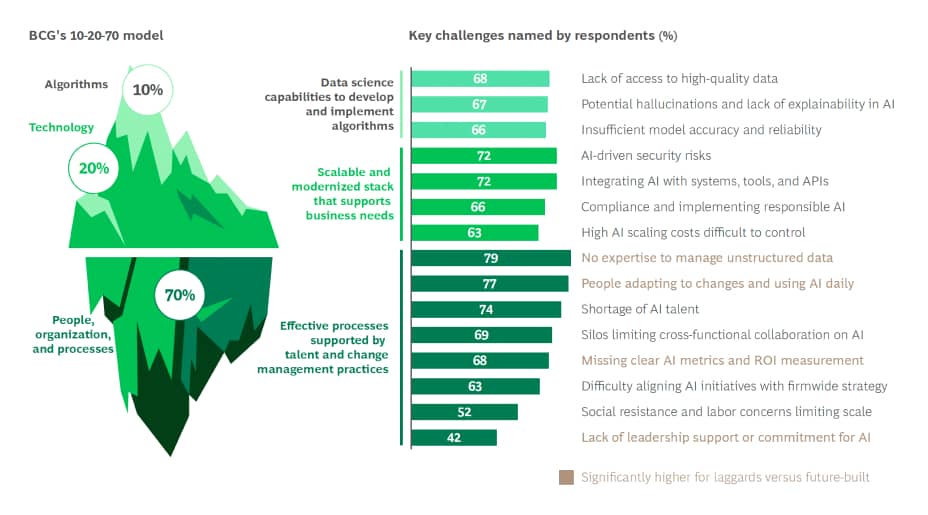
BCG research shows that AI adoption success now depends less on budget and more on organisational factors—people, processes, and how companies structure their operations.
AI implementation introduces operational complexities beyond technical integration. Organizations must redesign workflows, retrain staff, establish governance frameworks, and manage unpredictable costs.
The "human-in-the-loop" requirement can create operational bottlenecks. AI outputs require validation, especially in regulated industries, thereby reducing expected productivity gains and increasing operational costs.
A Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) research showed that resource allocation often misaligns with actual ROI, with most budgets concentrated in low-return areas such as sales and marketing rather than in high-return back-office automation.
Change management is another operational hurdle. Teams with diverse backgrounds, such as software engineers, data scientists, statisticians, and domain experts, may have different security practices and expectations. ICO guidance notes that security practices and expectations vary significantly, and some team members may have a limited understanding of broader compliance requirements.
The AI ROI disconnect
Many AI companies remain unprofitable. The previously mentioned MIT study found that, despite $30–40 billion in enterprise investment in GenAI, 95% of organizations (285 of 300) report no return on investment.
According to the research, the core issue isn't the quality of AI models but rather a "learning gap" across tools and organizations. Generic tools like ChatGPT work well for individuals because of their flexibility. However, they stall in enterprise settings because they don't learn from or adapt to specific workflows.
The research also uncovers a critical problem in resource allocation. More than half of GenAI budgets go to sales and marketing tools, yet the biggest ROI comes from back-office automation—eliminating business process outsourcing, cutting external agency costs, and simplifying operations, as stated in Fortune.
An additional factor contributing to failure is the build-vs-buy decision. According to Trullion's analysis of the MIT data, specialized vendor-led projects succeed approximately 67% of the time, while internal builds succeed only 33% of the time.
Companies often underestimate the complexity of integration and adoption when building in-house. Many outsourcing vendors claiming to offer AI-driven value might be overselling what they can deliver. Others may not fully understand the challenges of putting AI into practice. On the flip side, some companies jump into AI projects just to keep up with competitors, not because they have specific business goals in mind.
Failure often follows predictable patterns. Projects focus on flashy use cases rather than on fundamentals such as data quality and workflow integration. Poor data and rigid processes undermine initiatives before model performance matters. Without proper training, governance, and clear ROI goals, even strong tools struggle to gain adoption.
Data privacy and security risks
According to Stanford's 2025 AI Index report, AI-related privacy and security incidents jumped by 56.4% in a single year, with 233 reported cases throughout 2024.
IBM research highlights that AI privacy risks stem from the sheer volume of information involved - terabytes or petabytes of training data inevitably contain sensitive data such as healthcare records, personal data from social media, and biometric data. AI models poisoning, prompt injection attacks, and sensitive data leakage can expose proprietary information.
Companies also must navigate complex regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and industry-specific requirements when selecting AI vendors. Varying data residency rules complicate vendor selection for global organizations. Assessing how providers manage data across regions is essential to due diligence.
AI quality and ethical risks
AI solutions often produce outputs that appear convincing but may be incorrect, biased, or misleading. These quality issues create operational and reputational risks across industries. Hallucinations remain a persistent problem in generative AI. Models fabricate information, citations, and data points that can mislead decision-makers.
Bias in AI training data amplifies existing inequalities, as it often contains gaps and inconsistent quality. These limitations reinforce inequalities and generate biased outputs.
Compliance and the evolving regulatory landscape
AI regulation is accelerating globally, creating compliance uncertainty for organizations with existing AI deployments. Companies must prepare for requirements that could fundamentally change how they use AI.
The EU AI Act, which began enforcement in 2025, establishes risk-based requirements affecting vendors and users globally. High-risk AI systems face strict obligations around transparency, human oversight, and documentation.
Sector-specific regulations are emerging rapidly. Financial services face requirements under the DORA (Digital Operational Resilience Act), which sets strict obligations on ICT risk management and third-party oversight, affecting over 160,000 organizations in the EU. Healthcare, insurance, and other regulated industries face similar specialized frameworks.
Compliance costs for these frameworks may eliminate ROI for certain AI solutions. Organizations must keep comprehensive audit trails, conduct regular risk assessments, and demonstrate ongoing monitoring, which creates significant administrative overhead.
Economic and workforce implications
AI adoption creates economic ripple effects that extend outside individual organizations, influencing workforce dynamics, market stability, and productivity expectations.
A mismatch between productivity expectations and reality is creating organizational tension. Leadership expects AI to deliver immediate efficiency gains, but implementation frequently involves lengthy learning curves and workflow redesign. This gap strains budgets and patience.
Workforce displacement is already underway, particularly in customer support and administrative functions. Rather than mass layoffs, companies are increasingly not backfilling vacant positions. This pattern focuses on roles previously outsourced because of perceived low value, resulting in gradual but significant employment shifts.
How to choose the right AI development partner
Vendor selection is one of the most important decisions an organization can make when pursuing AI adoption. Here are the key criteria to consider.
AI projects often fail when vendors treat every industry the same. Seek a partner with proven experience in your domain. Domain knowledge shapes model design, data selection, and output validation. A team that understands your industry's data, workflows, and regulatory environment will deliver better outcomes than a generalist provider.
There are vendors that specialize in only one part of the AI lifecycle, such as model building, but not integration with existing systems. This creates gaps your internal team must address. The right partner supports every stage, from ideation and feasibility assessment to implementation, integration, and ongoing maintenance. This approach reduces handoff risks, maintains accountability, and ensures the solution works in production.
AI development does not exist in isolation. Models must integrate into real systems, handle large data volumes, and perform reliably under operational conditions. Choose a partner that combines artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data science expertise with strong software engineering capabilities. This combination distinguishes a working prototype from a production-grade solution.
Given the data privacy, regulatory, and security risks discussed in this article, compliance cannot be an afterthought. Select an AI vendor that treats cybersecurity and regulatory compliance as integral to development. This is especially important in regulated industries such as financial services, healthcare, and insurance, where the cost of non-compliance far exceeds the cost of proper implementation.
A key warning sign in AI outsourcing is a vendor that overpromises. As this article shows, most AI projects fail due to misaligned expectations, poor data readiness, and inadequate change management. The right partner will ask difficult questions upfront, assess your organization's readiness honestly, and set realistic timelines and ROI expectations, even if the answers are not what you want to hear.
The risks outlined in this article are real, but they are manageable with the right partner, the right approach, and a clear understanding of what success looks like for your business.
Navigating AI development requires more than evaluating technology. Choosing the right partner is a critical decision. It determines whether AI is a genuine fit for your organisation's needs, implemented properly, and aligned with your security and compliance requirements.

AI adoption risks FAQ
Start the risk management process by assessing your organization's data readiness, compliance needs, and internal capabilities before selecting a vendor. Establish clear governance, define required human oversight for AI outputs, and set realistic ROI expectations. Choose an AI outsourcing provider with industry experience and a strong focus on quality control, security, and compliance to reduce technical and operational risks.
Select an outsourcing partner that prioritizes security and compliance throughout development. Confirm how they manage data residency, data encryption, access controls, and compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA. Regular security audits, clear data processing agreements, consistent risk management practices, and transparent governance are essential safeguards.
AI systems can produce incorrect, biased, or misleading outputs, especially in complex or specialized contexts. Human oversight ensures AI-generated decisions are validated before affecting business outcomes, customer experience, or compliance. Many industries also require meaningful human control over high-risk AI systems to meet regulatory requirements.
Developing AI in-house requires significant investment in talent, infrastructure, and time. AI development outsourcing offers faster access to specialized expertise and proven frameworks, without the ongoing costs of an internal team. It also allows organizations to scale AI initiatives quickly and focus resources on core business priorities.
Key applications include automating repetitive tasks, developing predictive analytics and forecasting tools to aid operational decision-making, creating conversational AI and AI agents, and integrating machine learning into enterprise systems.
Related Insights








Inconsistencies may occur.
The breadth of knowledge and understanding that ELEKS has within its walls allows us to leverage that expertise to make superior deliverables for our customers. When you work with ELEKS, you are working with the top 1% of the aptitude and engineering excellence of the whole country.

Right from the start, we really liked ELEKS’ commitment and engagement. They came to us with their best people to try to understand our context, our business idea, and developed the first prototype with us. They were very professional and very customer oriented. I think, without ELEKS it probably would not have been possible to have such a successful product in such a short period of time.

ELEKS has been involved in the development of a number of our consumer-facing websites and mobile applications that allow our customers to easily track their shipments, get the information they need as well as stay in touch with us. We’ve appreciated the level of ELEKS’ expertise, responsiveness and attention to details.