
In a digital environment where product design and development need to keep pace with changing requirements, traditional prototyping approaches have clear drawbacks. Methods relying on static designs and basic clickable mock-ups can result in misalignments and additional work later on.
AI-based functional concepts offer an alternative by creating an interactive prototype that incorporates real logic, data, and backend elements. This method supports a building-first approach, where teams construct working models early rather than focusing heavily on upfront planning. Let’s take a closer look at why this shift is practical, how it adds value from a business standpoint, and its role in supporting aspects of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC).
- Traditional static prototyping often leads to costly delays caused by misaligned expectations and rework.
- AI-driven functional concepts allow teams to build interactive prototypes with real logic, data, and backend integrations starting from day one.
- Instead of making changes to processes, AI-based prototyping can be strategically incorporated into existing SDLC phases.
Traditional prototyping & its drawbacks
Traditional prototyping typically involves using tools like Figma to create visuals and simple interactions. While these approaches are useful, they often prioritise extensive planning, requirements gathering, workflow documentation, and design alignment before any functional validation.
This planning-heavy process can lead to several issues. Stakeholders may interpret static elements differently, creating uncertainty about system logic and behaviour. When implementation begins, unexpected technical challenges can arise, causing delays and increased costs.
From a business view, this creates inefficiencies. Executives looking for reliable progress need more than visuals; they require demonstrations of how systems handle data and logic in practice. Without early functional testing, teams risk building on flawed foundations, which can slow time-to-market in fields like fintech, healthcare, and manufacturing.

AI-based functional concept: prioritising building over planning
AI-based functional concepts shift the focus to building working prototypes from the outset. Rather than spending weeks on plans and then testing static mock-ups, teams use AI to create deployable applications that include business logic, data operations, and integrations early in the process.
This building-first method allows for quick construction of interactive models that reflect real operations, such as end-to-end flows with actual data. It reduces the time spent on theoretical planning by enabling immediate testing and refinement. As outlined in guides on AI-assisted development, using AI through structured prompts helps break down tasks and generate code iteratively, promoting a modular approach where components are built and validated step by step.
- Key elements include:
-
- User interactions: operations like create, read, update, and delete, supported by real databases.
- Backend support: quickly set up APIs and authentication using cloud development environments.
- Behavioural logic: flows that handle conditions and validations, potentially with AI elements.
This approach minimises the gap between ideation and execution, allowing teams to test ideas with minimal initial planning.
Business benefits of a building-first approach
Improved alignment and faster decisions
Lengthy planning phases can delay consensus, as stakeholders rely on abstract descriptions. Building functional concepts early lets everyone engage with prototypes, directly interacting with features and seeing results in action. This leads to clearer understanding and quicker decisions, often reducing alignment time by up to half.
Early feasibility checks and lower risks
Identifying issues late in planning is costly. By building prototypes with real elements upfront, teams can spot technical limitations early, such as integration problems. This helps in directing efforts toward feasible ideas, potentially cutting delivery risks by 30-50%, according to ELEKS' team estimates based on initial research and investigation conducted while preparing functional concepts.
Quicker validation and resource efficiency
According to our team, building-first shortens the path from idea to first increment, often from 2-4 weeks to 1-2 weeks. AI aids in generating code and structuring elements, supporting rapid feedback loops that trim unnecessary features. This can lower prototyping costs significantly and speed up overall development.
Please note that specific time estimates vary depending on the individual characteristics of each project. Reach out via our contact form, and our experts will provide you with personalised estimates or set up clarification workshops if needed.
Support for ongoing development
Prototypes built this way can evolve more easily, maintaining consistency through shared systems. For businesses, this means products that are adaptable, with reduced long-term costs.
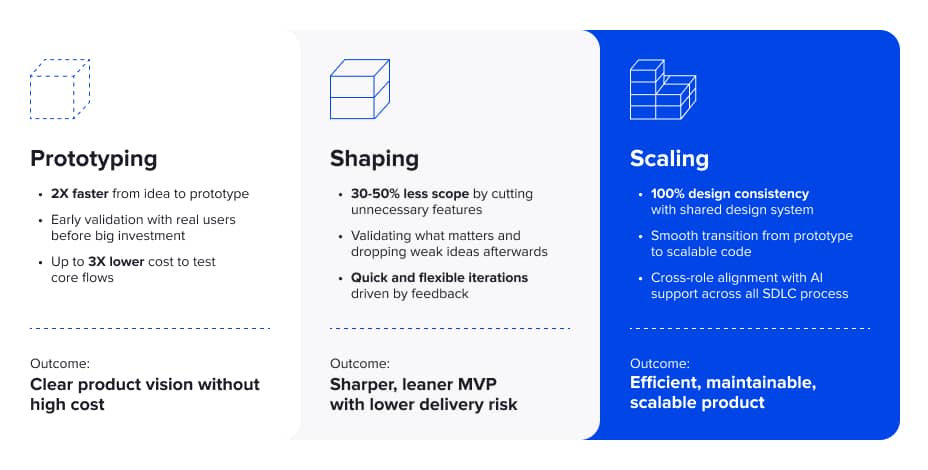
All numbers are based on the initial research and investigation conducted by the ELEKS team during the preparation of the functional concept.
Application of functional concepts in SDLC
Functional concepts can enhance specific parts of the SDLC without requiring a full overhaul. For instance, in requirements and design phases, an AI tool can help generate initial structures and flows, allowing teams to build prototypes that inform planning. During implementation, these prototypes serve as starting points for code, with AI coding tools assisting in logic and testing.
In testing and deployment, the working models enable early validation, making iterations more straightforward. This targeted use of AI prototyping supports a more efficient SDLC by incorporating building-first elements where they add value, such as accelerating feedback in agile setups. Resources on AI in software development note that tools like LLMs can automate tasks across phases, improving speed by 40-50% in focused areas, according to our team's analysis.
- Tools enabling functional concepts:
-
- Figma Make and Lovable: Turn designs into a functional prototype with logic and integrations.
- Supabase: Provides backend elements like databases and APIs.
- Claude and LLMs: AI tools aid in task breakdown and code generation.
The process involves designing basics, building with AI tools, connecting backends, and refining based on tests.
Conclusions
Functional concepts based on AI do not simply improve the prototyping process but change the way teams approach product development. By moving from methodologies that involve intensive planning to strategies that build functional prototypes, organisations can reduce rework, accelerate time to market by several weeks, and make more informed decisions through early functional validation.
As companies face increasing pressure to innovate quickly while minimising risk, AI prototyping offers a proven path to more efficient and cost-effective product development that meets market demands.

FAQs
Early validation, less rework (30-50% reduction), and shorter timelines for faster market entry.
We provide tools and expertise to build prototypes that fit into existing processes and help teams master AI prototyping tools for their specific requirements.
Yes, it's adaptable for areas like supply chain, fintech, and healthcare, needing quick validation.
AI prototyping is the process of using AI tools to create an early, simplified version of a solution to test its feasibility, functionality, and value before beginning full-scale development. Instead of creating a complete system, teams use prototypes to test basic ideas, test user interactions, and evaluate data requirements.
AI prototyping tools like Bolt, Lovable, v0, and Replit have emerged as significant resources for product managers in recent months. The choice of prototyping tool depends on your team's needs, whether you're building quick prototypes or need to code directly for more complex applications.
ChatGPT can help create prototypes for early ideas. It can write code prototypes, such as web apps and APIs. It can also outline UI and UX flows or draft chatbot interactions. This method works well for creating quick drafts, but such an AI prototype will need improvements in design and development before it can be used in production.
Related Insights









Inconsistencies may occur.
The breadth of knowledge and understanding that ELEKS has within its walls allows us to leverage that expertise to make superior deliverables for our customers. When you work with ELEKS, you are working with the top 1% of the aptitude and engineering excellence of the whole country.

Right from the start, we really liked ELEKS’ commitment and engagement. They came to us with their best people to try to understand our context, our business idea, and developed the first prototype with us. They were very professional and very customer oriented. I think, without ELEKS it probably would not have been possible to have such a successful product in such a short period of time.

ELEKS has been involved in the development of a number of our consumer-facing websites and mobile applications that allow our customers to easily track their shipments, get the information they need as well as stay in touch with us. We’ve appreciated the level of ELEKS’ expertise, responsiveness and attention to details.

