
In which case you’d know that since its introduction in 2008, Bitcoin has risen in value. Like really, it has: in its infancy, during negotiating the possible value of transactions on the bitcointalk forums, one notable transaction of 10,000 BTC was used to purchase two pizzas. Today 10,000 BTC equals to over 35 million dollars. This growth was achieved in less than 10 years.
Now before we get carried away, one could point out that the brave new currency was designed as a “Peer-to-Peer” system relying on “cryptography to control its creation and management, rather than on central authorities”. And its design borrows ideas from the cypherpunk community. So sounds like the opposite of what businesses should be interested in, right? A skeptic would bring up Bitcoin’s motley history of being oppressed by regulatory authorities or even barely legal.
And yet, if you’re still confusing cyber-punk fantasy and cypherpunk community, here is a puzzling list of companies that deal with bitcoins, and it includes such likely familiar names as Microsoft, IBM, Reddit, Subway, Lionsgate Films, Bloomberg.com, WordPress.com, Wikipedia, Steam, Richard Branson’s Virgin Galactic, and Tesla. Oh, and Bitcoin is now accepted as a legal payment method in Japan.
Now would be a good time to wonder why businesses are starting to pay attention and governments are beginning to take digital currency into account and making standards for it rather than suppressing it. The answer is in the principle behind it and, ironically, in the security, it provides to the user. Bitcoin network is fully decentralised and is meant to exclude trust-reliance and intermediaries from the financial operations: a direct transaction between users recorded in a public ledger. No single party has the power to issue new bitcoins or approve Bitcoin transactions. The shared transaction register is called the blockchain. And it’s this technology that is of particular interest to businesses.
While bitcoin as an equity is still difficult to project surely enough to view as an investment, its success key, blockchain technology, can and should be used for business processes improvement. Today, distributed ledger technology can be tailored by professional blockchain software developers for various business optimisations. The technology is basically a game changer, a principle of organising human interactions in a secure and yet completely decentralised way, which could have applications in far more than just the financial sector.
Blockchain, as put by the Harvard Business Review, is a foundational technology that "has the potential to create new foundations for our economic and social systems. " They call it foundational due to the fact that the changes it is expected to bring about are not rapid – but very tenacious and large-scale. For comparison, they offer the 30-year path that took TCP/IP technology (yes, the Internet) to success: “it took more than 30 years for TCP/IP to move through all the phases—single use, localised use, substitution, and transformation—and reshape the economy. Today, more than half the world’s most valuable public companies have internet-driven, platform-based business models”.
So how does it work and what are the benefits?
Much like TCP/IP drastically lowered the cost of connections, blockchain has the capacity to reduce the cost of transactions, which makes it a very efficient system of record. Tracking and recording continuous transactions, analysing performance rates based on those and making plans for future – all of those processes are inalienable for a business. Most businesses have no single compound record of all the activities; instead, data are distributed across internal units and then reconciled across ledgers, which takes time and leaves space for human error.
So, what is blockchain and how it can be a solution here? In simple words, blockchain is just a way of handling databases, the ultimate ledger. Only a highly efficient, secure and verifiable one. In a regular enterprise software system, there are numerous dissimilar databases for various activities of a company: changes to them are made separately, and then you spend resources to compile the whole thing together. This is, in terms of resources, the opposite of optimal and efficient.
In a blockchain system, the ledger is replicated in identical databases, hosted and maintained separately. When changes are entered in one copy, all the other copies are simultaneously updated. This smart business approach would keep records of exchanged assets in all ledgers. “If a stock transaction took place on a blockchain-based system, it would be settled within seconds, securely and verifiably”, the Harvard Business Review explains.
Secure, decentralized, shared publicly, trusted and automated. This is exactly the kind of solution that modern professionals would want and software developers would be looking to develop. The most important fact about blockchain is that its applications are not limited to the banking and financial industry – its principle can be used for other business improvement purposes, including smart contracts or establishing a secure document transfer system, network infrastructure or marketing forecasts and many others.
For example, blockchain allows creating a custom system for smart documents management: secure storing and transfer of various kinds of assets.
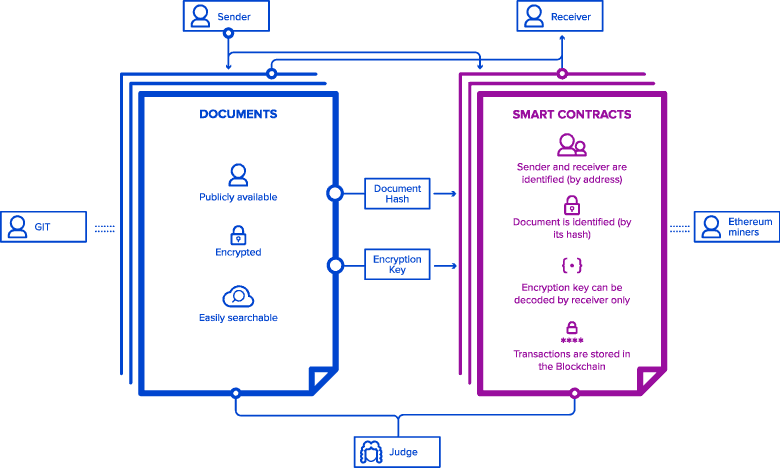
In establishing secure document transfer networks, blockchain provides an invaluable advantage because of efficient cryptography and a decentralised structure. This sets the foundation for broadening the scope of typical smart contracts from just the financial sector to the legal realm, real estate, intellectual property and much more.
Whether you need to improve identification and authentication solutions or introduce a supply chain verification system, or shared economy solutions for, say, ride-sharing services – there’s a whole new frontier in business systems organisation.
Let’s discuss how your organization can take full advantage of blockchain’s benefits.
Related Insights







The breadth of knowledge and understanding that ELEKS has within its walls allows us to leverage that expertise to make superior deliverables for our customers. When you work with ELEKS, you are working with the top 1% of the aptitude and engineering excellence of the whole country.

Right from the start, we really liked ELEKS’ commitment and engagement. They came to us with their best people to try to understand our context, our business idea, and developed the first prototype with us. They were very professional and very customer oriented. I think, without ELEKS it probably would not have been possible to have such a successful product in such a short period of time.

ELEKS has been involved in the development of a number of our consumer-facing websites and mobile applications that allow our customers to easily track their shipments, get the information they need as well as stay in touch with us. We’ve appreciated the level of ELEKS’ expertise, responsiveness and attention to details.

