With the fast-paced digitalisation of every aspect of human life, even government agencies are making efforts to utilise digital technologies in their operations by using dedicated government software solutions. This enables government agencies to automate processes, handling public records with significantly fewer resources, thereby saving public funds. At the same time, in the age of increasingly rising cyber threats, public organisations face multiple challenges in securing their data and systems from potential breaches.
Ongoing efforts to boost digital transformation initiatives in the public sector often need to consider how independent their systems must be to not only fulfil cybersecurity needs but also to be as resilient and compliant as possible. Those needs are one of the cornerstones of digital sovereignty. In this article, we will discuss how government resources are migrating to digital tools, what this term means, and how those practices can be applied.
- Digital transformation in government operations by automating processes and replacing paper-based workflows with digital solutions saves public funds and reduces administrative overhead.
- There are multiple successful real-life examples on how digital transformation in governments enables better operational efficiency and improves citizen relations.
- Digital sovereignty is becoming a critical factor in the development of new technologies for both the public and private sectors.
- Governments must strategically invest in self-reliant digital ecosystems that ensure security, resilience, and future-proofing.
What is government digital transformation?
Digital transformation in public sector organisations refers to modernising how government software is used to operate, deliver, and interact with citizens and businesses, replacing traditional paper-based and manual tasks with digital and automated workflows.
Thanks to this approach, existing government agency processes are transitioned to dedicated government software, such as online portals, mobile apps, and other digital tools that process, store, and analyse official documents and records. Very often, the entire process includes legacy software modernisation to align existing systems with new features in the e-government technological stack. In this way, government employees can more effectively deliver public services by reducing delays and administrative overhead, access a more detailed overview of public data, and process it in more sophisticated ways to view statistics or enable predictive analytics.
What are examples of government digital transformation projects?
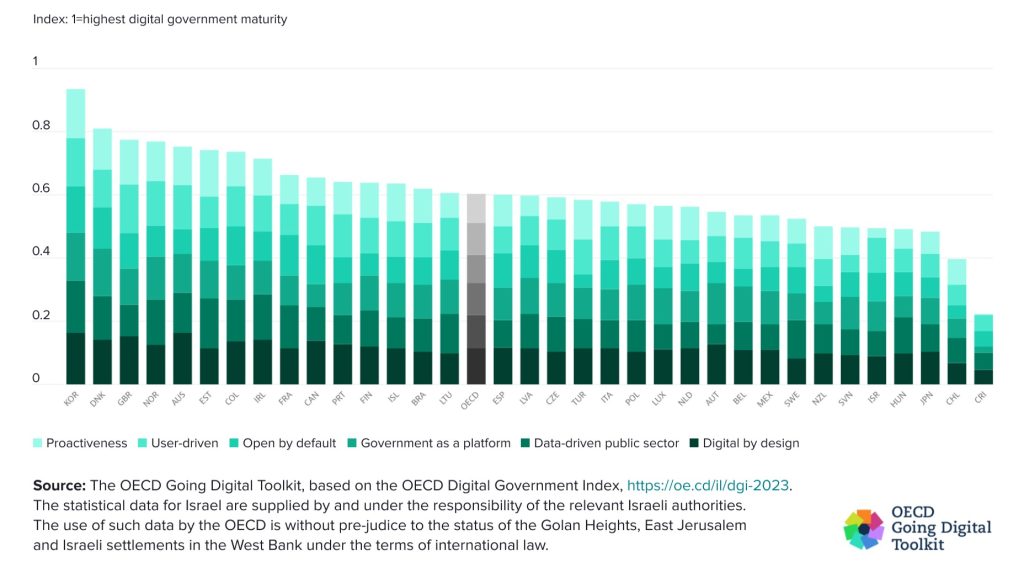
Currently, around the world, multiple existing GovTech solutions serve as fully functional examples of how digital government can improve service delivery. According to the Digital Government Index created by the OECD, South Korea is the most digitally advanced government, utilising state-of-the-art technical solutions. One of the reasons behind this is that South Korean digitalisation efforts began back in the 1980s. Alongside this country's technological advancements, most government agencies gradually transitioned to operating with emerging technologies eliminating the need for paperwork.
"Digital government is essential to transform government processes and services in ways that improve the responsiveness and reliability of the public sector. The OECD Digital Government Index assesses countries' digital government by looking at the comprehensiveness of strategies and initiatives in place to be able to leverage data and technology to deliver a whole-of-government and human-centric digital transformation of the public sector. The assessment is based on the six dimensions of the OECD Digital Government Policy Framework: 1) digital by design, 2) data-driven public sector, 3) government as a platform, 4) open by default, 5) user-driven, and 6) proactiveness (see notes). The DGI is a composite index that takes values from 0 to 1, where 1 indicates the highest digital government maturity and 0 indicates low and/or fragmented progress across organisations."
Other successful digital transformation initiatives include:
- The Estonian program e-Estonia, since December 2024, is allowing its citizens to complete 100% of public services online.
- The Ukrainian app Diia hosts 40 government services, including tax payment, car registration, and marriage applications, making it one of the most advanced digital government services in the world.
- Singapore, with its Smart Nation Initiative that uses many advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and data analytics, is on its way to becoming not only one of the most digitalised nations but also a smart city that is constantly improving the standard of living of its citizens.
- The e-Excise system recently adopted by the Ukrainian government is a digital platform co-designed by ELEKS to track and monitor excisable goods, such as alcohol and tobacco, to prevent tax evasion and illegal trade. It is part of Ukraine's broader effort to digitise public administration and improve transparency in the tax system.
What are the benefits of the digital transformation of the public sector?
- Better efficiency - introducing digital systems to public services can drastically improve efficiency and accessibility of government operations. That way, citizens are allowed to interact with their government through 24/7 available portals optimised for mobile devices, instead of relying on paper records or legacy systems and needing to visit official institutions in person to settle official matters. This approach might also reduce the public workforce needed to process all necessary documents or generate reports.
- Cost savings - government software solutions are generating less costs through e.g. document processing automation or fewer human resources needed
- Better data-driven decisions - Integrating digital services in the public sector enables government employees to access real-time data analytics and insights, facilitating evidence-based policymaking.
- Greater flexibility - digital government infrastructure empowers more agile service delivery in case of rapidly changing citizen needs or fast incident response with better resource allocation.
What are examples of digital sovereignty initiatives?
Currently, multiple ongoing initiatives are underway to achieve greater digital sovereignty, particularly among EU countries seeking to reduce their dependence on foreign technologies. The most recent ones involve:
- French and German governments are leading to the development of a roadmap to create the so-called Eurostack by establishing the European Sovereignty Fund that will allow EU countries to create their own technological solutions independently from US and Asian providers. Plans include investments in semiconductors, cloud solutions, and AI that will be fully owned by European organisations.
- The Dutch government is planning to build a fully independent cloud infrastructure as an alternative to US-owned solutions like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
- The Danish Ministry of Digitalisation announced that the country's institutions will be moving from Microsoft to open-source solutions like LibreOffice and Linux to reduce dependency on foreign technologies.
Conclusion
Digital transformation efforts to modernise government legacy systems and enhance public sector capabilities, while meeting the demand for efficient operations, are currently one of the critical challenges for most government agencies. With the new tools embedded in GovTech that enable public sector employees to operate efficiently with the help of data visualisation, better performance tracking can significantly streamline processes in official institutions.
In addition, governments need to strike a balance between self-reliance and innovation to secure digital sovereignty, ensuring the resilience and independence of these systems. It requires significant public funds transfers to secure strategic control over data, infrastructure, and software, thereby reducing reliance on foreign providers. But with those precautions, governments can build digital ecosystems that not only take better care of their citizens and are more efficient but also secure and future-proof.

FAQs
To select the right digital government transformation service provider, the main focus should be on reviewing: proven experience in public sector projects, strong data security and compliance standards, and wide abilities for modernising legacy systems.
Key challenges include higher initial costs of building fully sovereign solutions, potential slow adaptation of developed systems, limited technical expertise, and a need to support multiple internal systems to preserve independence. Additionally, those projects require the involvement of multiple stakeholders and a high level of compliance with local laws. With proper project planning, most of those risks can be avoided or minimised.
Key technologies needed to fulfil digital sovereignty goals include cloud infrastructure, national digital identity platforms, extensive cybersecurity solutions, resilient telecommunications networks, data centres, and AI systems that can operate fully independently when needed.
The time needed to introduce e-government solutions widely depends on the scope of the project and existing infrastructure. If those initiatives involve additional solutions to make systems digitally sovereign, which require many additional features, those programs might often use phased implementations with gradual rollouts.
Depending on the technological stack and project size, the costs of these investments may be very high, especially when the current digital infrastructure is not fully sufficient. However, those initial expenses, when compared to long-term benefits, might overall reduce operational costs.
Related Insights









Inconsistencies may occur.
The breadth of knowledge and understanding that ELEKS has within its walls allows us to leverage that expertise to make superior deliverables for our customers. When you work with ELEKS, you are working with the top 1% of the aptitude and engineering excellence of the whole country.

Right from the start, we really liked ELEKS’ commitment and engagement. They came to us with their best people to try to understand our context, our business idea, and developed the first prototype with us. They were very professional and very customer oriented. I think, without ELEKS it probably would not have been possible to have such a successful product in such a short period of time.

ELEKS has been involved in the development of a number of our consumer-facing websites and mobile applications that allow our customers to easily track their shipments, get the information they need as well as stay in touch with us. We’ve appreciated the level of ELEKS’ expertise, responsiveness and attention to details.