
- Mainstream use of XR technology is slow because of several hardware issues. These include heavy headsets, safety concerns due to blocked vision, social awkwardness, and limited interactivity.
- Lightweight AR glasses that provide unobstructed, hands-free functionality are strong candidates for wide adoption.
- XR is useful in areas like training employees, simulating healthcare situations, and providing services in industrial settings, where the controlled environments help ease the technology's current limitations.
What is XR and why hasn't it lived up to the hype (yet)?
Extended Reality (XR) has long been touted as the 'next big thing,' but it still remains relatively niche. To understand why, let's first clarify what XR actually is. XR is the umbrella term for tech that lets us interact with information and products in more natural ways than just staring at screens.
So, on one end, we've got virtual reality, or VR, full immersion. The user puts on a headset, like a Valve Index or an HTC Vive, and you're in a completely virtual space.
Great for gaming, definitely, and for high-stakes training, simulations, stuff like that. But the problem, historically, these were pretty niche devices, purpose-built. They never achieved mass adoption, which limited the growth of their software ecosystem. In addition, VR experiences are associated with causing motion sickness, even now, when VR headsets have gotten a lot better.
Then we have augmented reality, or AR. This is where digital things get layered onto our real-world view. Think of glasses with transparent lenses, like the Microsoft HoloLens or Magic Leap 2. AR has mostly been aimed at the enterprise market for things like remote assistance for technicians, industrial training, and visualising medical scans. But again, it stayed niche, due to high costs, a narrow field of view, and limited consumer use cases.
And last term under XR is mixed reality, MR, which seems to be gaining steam now, using cameras to blend digital and real, like Meta Quest 3/3s and Apple Vision Pro. High-quality cameras on the outside of a headset capture the real world, and then digital objects are convincingly placed within that real-world view. It sort of blends the strengths of VR and AR. Blending VR and AR into one device creates a versatile platform which can handle all sorts of activities like watching content, getting work done, staying fit, meditating, and much more. However, even with all this potential, there are still some challenges that this technology has to deal with, which are explained below.
- Key reasons XR Headsets still struggle to break into the mainstream:
-
- Heavy. Current headsets are too heavy for long periods, creating neck strain and fatigue that make them unsuitable for the hours-long usage patterns that define successful computing platforms.
- Unsafe. While both technologies allow users to see their surroundings, if the video feed glitches or suddenly cuts out in a headset, this creates a significant safety risk, as the user is left temporarily blinded or disoriented.
- Socially unacceptable. XR devices can feel pretty awkward in social situations. Just imagine trying to chat with someone who's got a big headset on during a face-to-face conversation.
- Limited interactions. XR devices often require the use of controllers for precise movements. Alternatively, you can use hand tracking by waving in front of the camera, which can get tiring quickly. After five minutes, you may prefer your laptop, where a simple finger movement gives you the same results.
- Mostly indoor usage. A lot of XR experiences are designed for controlled indoor spaces, which really narrows their practicality.
How are XR devices becoming an everyday-use technology?
Meta is shaking up the world of extended reality by moving away from those bulky headsets and focusing on sleek, lightweight AR solutions that fit effortlessly into everyday life. Their new game plan revolves around AR glasses that use micro-LED projection and eye-tracking tech. First prototypes also got a wireless compute puck that handles all the heavy processing, keeping the glasses light and easy to wear.
On top of that, there’s an EMG wristband that lets you control things with gestures, thanks to advanced neural interface technology. This technology allows you to interact with XR interfaces and provide input in a much more intuitive and faster way than in existing XR headsets. No need for controllers, no need to hold your hands in front of you, no struggling to point at elements or tap keys on a floating keyboard.
Meta didn’t make any huge inventions, but they collected all the needed pieces of the puzzle – the technologies that finally make XR devices usable and comfortable. And by releasing the Meta Ray-Ban Display, they showed the world that such devices can be affordable. So, this new form factor for XR devices, smart glasses with displays, becomes a big deal for business.
Reasons AR glasses are becoming a new standard for the XR industry:
- They are lightweight, so you can wear them almost all day.
- They don’t have safety issues. Even if the battery runs out while driving, you'll still be able to see the road clearly, just without the digital overlay.
- The peripheral vision remains unobstructed, similar to regular glasses, so you'll be aware of what’s happening around you.
- They are safe to use outdoors and are designed to look like regular glasses; you won't feel awkward wearing them in public.
- Due to the neural wristband interface, interactions are intuitive and convenient. Your hands remain free, allowing you to control the interface with just a slight finger movement, even when holding tools, boxes, or other items.
- And they are ideal for working with AI, which was the original reason for investing in this form factor.
XR business applications beyond entertainment
XR technology is often in the news for its gaming and entertainment uses, but it can also make a big impact in other business areas.
Healthcare
With the help of AR in modern healthcare, the surgeon can see all the information about the patient right next to the incision site, without having to lift their head every time to look at the monitors. And they can interact with this interface with a simple flick of the finger, even if they are holding a clamp or a scalpel in their hand.
Navigation
XR devices can provide drivers with information about upcoming turns by displaying it directly above the road, similar to a road sign. This allows them to keep their eyes on the road without needing to look at their phone or screen. This feature would be particularly beneficial for nighttime driving, as the contours of the road and road signs can be overlaid on the real image.
Contextual guidance & reminders
AR/VR technology offers on-the-spot help to customers by helping them find their way around, track down vehicles, and get useful info about products, onboarding guidance, or even take interactive tours. This not only cuts down on support costs but also boosts the overall customer experience and engagement.
Enterprise training & simulation
Companies in industries like aviation, manufacturing, energy, and safety-critical sectors are using custom XR training platforms that let employees practice tricky or risky procedures in safe virtual settings. This approach not only cuts training costs but also boosts retention and safety.
Retail & e-commerce
AR try-on features and virtual showrooms have been around for quite a while now. With the help of this feature, shoppers can see how products look in their own space or try on clothes or apply makeup without setting foot in a store.
Industrial & field services
AR work instructions guide technicians through complicated maintenance tasks, and remote support lets experts lend a hand in real time. Combining IoT sensors with AR overlays gives a major boost to diagnostic and monitoring capabilities.

Practical XR applications: ELEKS’ case studies and project examples
Immersive car experiences
The challenge: We wanted to showcase car interiors in a way that would really grab attention while allowing for customisation details.
The solution: Our team created a cool WebGL-based app that mixes 3D visuals, mobile web tech, and VR features. Users can check out car interiors in 360-degree views using their device's gyroscope, switch up seating positions, and change seat materials and dashboard styles in real-time. Plus, it supports Google Cardboard for a complete VR experience.
Try before you buy
The challenge: Develop a realistic virtual try-on experience for glasses using user-recorded videos.
The solution: An AI-driven virtual try-on system uses smart algorithms to look at the videos users upload and figure out exactly how their heads are positioned and turned. With WebGL rendering, it adds realistic overlays of glasses, complete with reflections and shadows, so users get an authentic feel of how the glasses would actually look on them.
HoloLens for education
The challenge: Make education easier and more straightforward when it comes to dealing with complex equipment and important skills.
The solution: This education solution includes user logins, tests one can take on a mobile device, and interactive quizzes on HoloLens. The mobile app is built with Xamarin, making it easy to work across different platforms. It connects with the HoloLens app for those interactive tests and can even provide hints to make the experience even better.
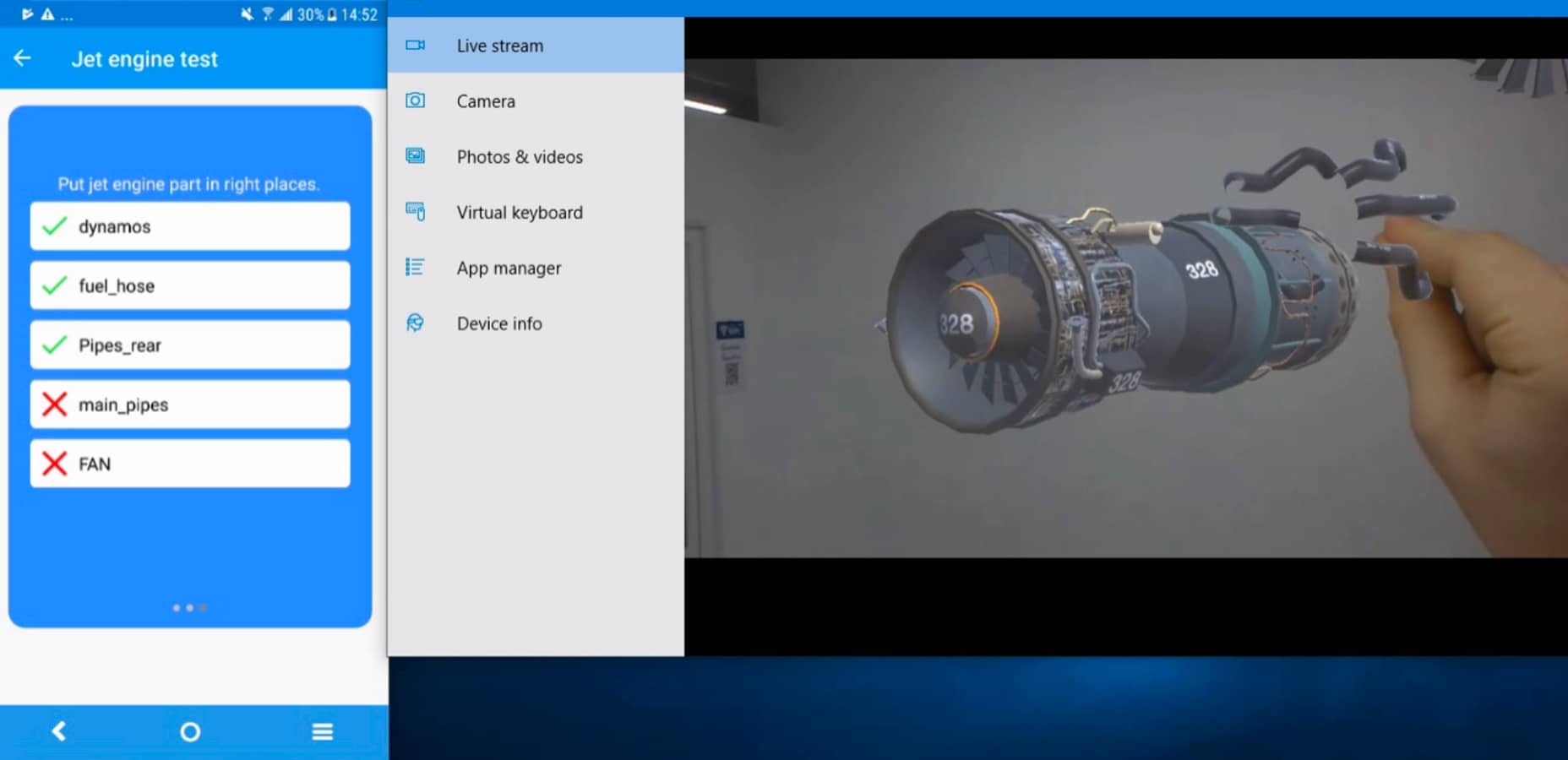
AR solution for trade show
The challenge: Prepare a solution that could help the client stand out from the competitors at a trade show and grab the attention of new customers.
The solution: After we found out that the customer is currently showcasing their merchandising products on paper, we designed an AR solution that provided a high-quality rendering of the merchandising stand, adjustable in scale and allowing for planning in real size.
Conclusions
So, how can businesses make the most of XR technology? The short answer: whenever a user needs to access information while their hands are busy.
When users need to receive information discreetly, XR glasses offer an ideal solution.
When it comes to training, these glasses can show instructions from the same viewpoint users will have when they're actually doing their tasks in the real world. Plus, in situations where there's a risk to health or equipment, XR can quickly provide vital information exactly where it's needed—something regular methods just can't keep up with.

FAQs
Examples of XR platforms that provide immersive experience capabilities include Meta Quest, Apple Vision Pro, and Microsoft HoloLens. These platforms are designed to efficiently handle multi-dimensional interactions generated by advanced display technologies for tasks like training and collaboration.
The main difference is that traditional training methods are optimised for passive learning and classroom environments, whereas XR training offers immersive learning support to efficiently deliver and practice complex procedures often requiring hands-on experience. Extended reality training uses specialised spatial computing algorithms to create realistic practice environments.
Video conferencing is a digital communication tool and does not natively provide immersive experience capabilities. While it supports remote collaboration, it lacks built-in features for managing three-dimensional interactions or performing spatial computing functions.
No, virtual reality is a subset of Extended Reality and does not encompass the full spectrum of immersive technologies. VR focuses specifically on fully virtual environments, while XR includes comprehensive reality solutions that blend physical and digital worlds through augmented and mixed reality technologies.
Immersive experience refers to digital interactions that engage multiple senses and create a sense of presence in virtual or augmented environments, often generated by XR technologies. These experiences capture user attention completely and are used in business applications for tasks like training and customer engagement.
Spatial computing is a technology framework that enables efficient processing of three-dimensional interactions to support immersive experience delivery. It plays a crucial role in Extended Reality applications by organising digital content for natural interaction based on spatial relationships.
Mixed Reality is a method of blending physical and digital worlds based on the integration of real and virtual elements, which represent hybrid environments combining physical spaces with digital overlays
Related Insights








Inconsistencies may occur.
The breadth of knowledge and understanding that ELEKS has within its walls allows us to leverage that expertise to make superior deliverables for our customers. When you work with ELEKS, you are working with the top 1% of the aptitude and engineering excellence of the whole country.

Right from the start, we really liked ELEKS’ commitment and engagement. They came to us with their best people to try to understand our context, our business idea, and developed the first prototype with us. They were very professional and very customer oriented. I think, without ELEKS it probably would not have been possible to have such a successful product in such a short period of time.

ELEKS has been involved in the development of a number of our consumer-facing websites and mobile applications that allow our customers to easily track their shipments, get the information they need as well as stay in touch with us. We’ve appreciated the level of ELEKS’ expertise, responsiveness and attention to details.

